What is Menorrhagia?
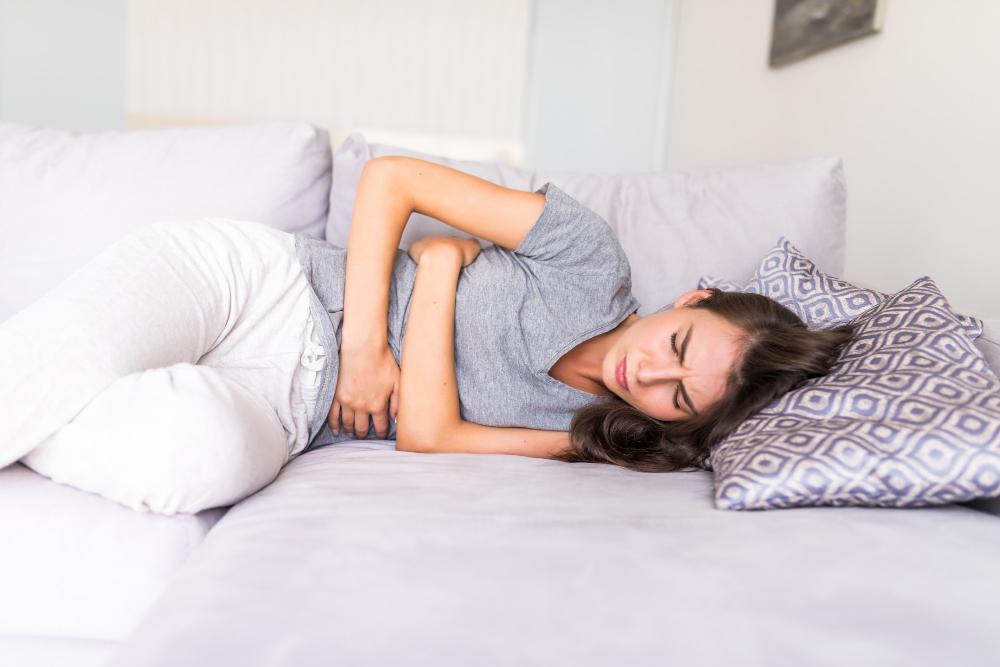
Menorrhagia means heavy or long-lasting menstrual bleeding. Many women experience some changes in their periods. However, menorrhagia is more than just a heavy flow. It can disrupt daily life and may signal an underlying health issue. According to the CDC, menorrhagia affects about one in five women in the United States. Because it can cause discomfort and even lead to anemia, understanding menorrhagia is important. Heavy menstrual bleeding is not something you have to live with. There are ways to manage and treat it.
Common Symptoms of Menorrhagia
Not all heavy periods mean you have menorrhagia. Still, certain signs can help you know when to seek help. For example, you may notice:
Sometimes, heavy periods can cause you to miss work or school. If you notice these symptoms, it may be time to talk to a doctor.
Causes of Menorrhagia
There are many causes of menorrhagia. Sometimes, the reason is clear. Other times, it is not. Common causes include:
Sometimes, no clear cause is found. Even so, treatment for menorrhagia is still possible.
How Menorrhagia is Diagnosed
Doctors use several steps to diagnose menorrhagia. First, they ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may perform a physical exam. In addition, you might need some tests, such as:
These tests help find the cause of heavy menstrual bleeding. With this information, your doctor can suggest the best treatment for menorrhagia.
Treatment Options for Menorrhagia
Treatment for menorrhagia depends on the cause, your age, and your health. For many women, simple changes or medicines can help. Common treatments include:
Sometimes, a combination of treatments works best. Your doctor will help you choose the right option.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Menorrhagia
While medical treatment is important, lifestyle changes can also help manage heavy periods. Here are some tips:
With these steps, you can feel more in control of your health.
Prevention and When to See a Doctor
Sometimes, menorrhagia cannot be prevented. However, early treatment can help avoid complications. You should see a doctor if you:
Early care can help you manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. According to the World Health Organization, seeking timely medical advice is key to women’s health.
In summary, menorrhagia is a common but treatable condition. If you experience heavy menstrual bleeding, it is important not to ignore it. At Dr. Meenal Singh, timely evaluation and treatment options are available to manage menorrhagia effectively.
For personalised advice on managing menorrhagia, consult Dr. Meenal Singh.