What is Polymenorrhea?
Polymenorrhea means having menstrual periods more often than usual. In most cases, a normal menstrual cycle lasts about 21 to 35 days. However, with polymenorrhea, periods come less than 21 days apart. As a result, women may notice frequent periods or short menstrual cycles. This condition can affect daily life and may signal an underlying health issue. Understanding polymenorrhea is important for women’s health and well-being.
Common Symptoms of Polymenorrhea
Many women with polymenorrhea notice changes in their periods. For example, they may have more than one period in a month. Other symptoms can include:
Sometimes, these symptoms can be mild. However, they may also cause stress or worry. If you notice these signs, it is important to pay attention to your cycle.
Causes and Risk Factors
Polymenorrhea can have many causes. Sometimes, it is due to natural changes in the body. For instance, teenagers and women nearing menopause may have irregular cycles. Other possible causes include:
Because there are many possible causes, it is important to find out what is affecting your cycle. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hormonal changes are a common reason for irregular menstruation.
How Polymenorrhea is Diagnosed
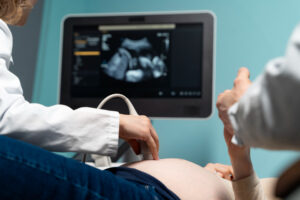
Doctors use several steps to diagnose polymenorrhea. First, they will ask about your menstrual history. For example, they may want to know how often your periods come and how heavy the bleeding is. Next, they may perform a physical exam. Sometimes, blood tests are needed to check hormone levels or rule out thyroid problems. In some cases, an ultrasound may be used to look at the ovaries and uterus. Keeping a period diary can help your doctor understand your cycle better. Early diagnosis can help find the cause and guide treatment.
Treatment Options for Polymenorrhea
Treatment for polymenorrhea depends on the cause. For many women, simple changes or medications can help. Common treatment options include:
In some cases, no treatment is needed if the condition is mild or temporary. However, it is always best to discuss options with a healthcare provider. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends regular check-ups for women with irregular periods.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While not all cases of polymenorrhea can be prevented, healthy habits may help. For instance, you can:
Additionally, avoiding sudden weight loss or gain can help keep your cycle regular. If you notice changes, early action can make a difference.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to know when to seek medical help. You should see a doctor if:
Early medical advice can help find the cause and prevent complications. Remember, frequent periods are not always normal. A healthcare provider can guide you to the right treatment.
In summary, polymenorrhea refers to having frequent periods or shorter menstrual cycles than normal. Though it can have several causes, most cases can be effectively managed with timely medical care and lifestyle adjustments.
For personalised guidance on managing polymenorrhea and restoring cycle balance, consult Dr. Meenal Singh, an experienced gynaecologist dedicated to women’s reproductive health.