Introduction
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a common concern for many women. It means bleeding from the uterus that is not part of a normal period. Sometimes, this bleeding is heavy, lasts too long, or happens at odd times. Because abnormal uterine bleeding can affect daily life, it is important to understand its causes and treatments. Knowing more helps women take charge of their health and seek help when needed.
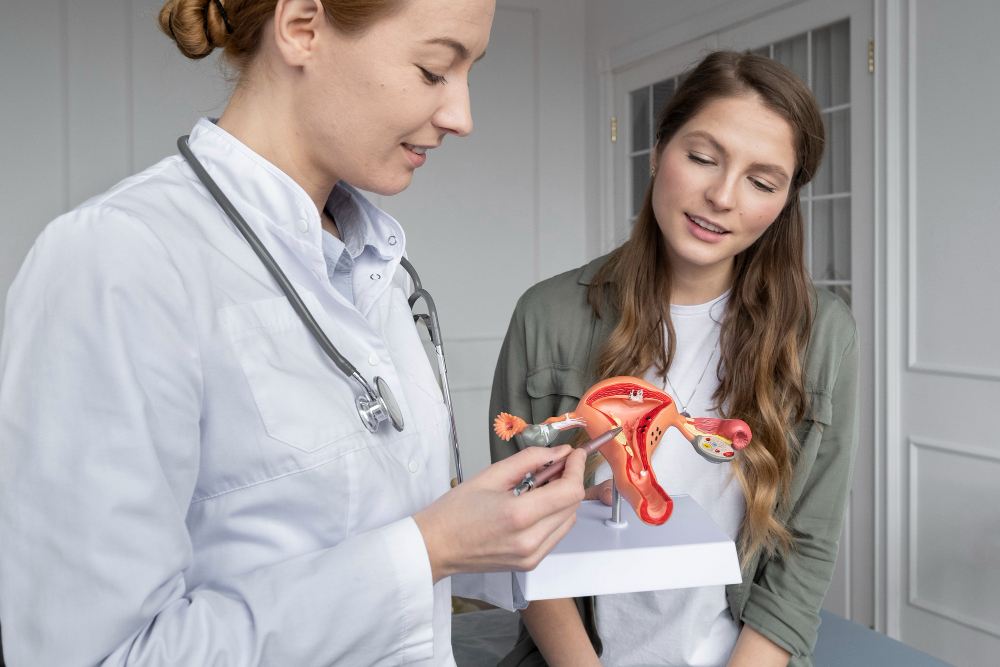
What is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding?
Abnormal uterine bleeding is any bleeding from the uterus that is not expected. For example, it may happen between periods, after sex, or after menopause. Sometimes, periods are much heavier or lighter than usual. In other cases, periods last longer or come more often. This condition can affect women of all ages, but it is most common during puberty and before menopause.
Common Symptoms
Many women notice changes in their periods. However, some signs may point to abnormal uterine bleeding. Look for these symptoms:
Because these symptoms can be caused by many things, it is important to track any changes. If you notice any of these signs, consider speaking with a doctor.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are many causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. Some are simple, while others need medical care. Common causes include:
Additionally, some women are at higher risk. For example, those with a family history of bleeding problems or those who are overweight may have a higher chance. Age also plays a role, as teens and women nearing menopause often have hormone changes that affect bleeding.
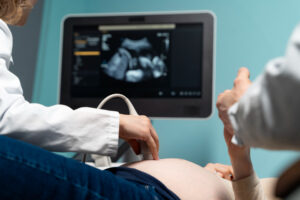
How is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Diagnosed?
Doctors use several steps to find the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding. First, they ask about your medical history and symptoms. Next, they may do a physical exam. Often, they will suggest tests such as:
Because each woman is different, your doctor will choose the best tests for you. Early diagnosis helps find the right treatment and rules out serious problems.
Treatment Options
Treatment for abnormal uterine bleeding depends on the cause. Sometimes, no treatment is needed if the problem is mild. However, many women need help to manage symptoms. Common treatments include:
Because every woman is unique, your doctor will help you choose the best option. In many cases, simple treatments can control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While not all cases can be prevented, some steps may help reduce the risk of abnormal uterine bleeding. Try these tips:
Additionally, regular check-ups can help catch problems early. If you notice changes, do not wait to seek advice.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to know when to get medical help. See a doctor if you have:
Because abnormal uterine bleeding can have many causes, only a doctor can find the right answer. Early care can prevent complications and help you feel better.
Conclusion
Abnormal uterine bleeding can be concerning, but timely care can make a big difference. If you experience changes in your menstrual cycle or unusually heavy bleeding, do not ignore it. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications and ensures effective treatment.
For personalised advice and expert care on abnormal uterine bleeding, consult Dr. Meenal Singh, an experienced gynaecologist dedicated to women’s health and hormonal balance.