Placenta previa is a pregnancy complication where the placenta covers part or all of the cervix. This condition can cause bleeding and may affect the health of both mother and baby. Because placenta previa can lead to serious problems, it is important to understand its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Early care helps ensure a safer pregnancy for everyone involved.
What Is Placenta Previa?
Placenta previa happens when the placenta sits low in the uterus and covers the cervix, either partly or completely. Normally, the placenta attaches higher up in the uterus. However, when it covers the cervix, it can block the baby’s way out during birth. As a result, placenta previa can cause bleeding, especially in the second or third trimester. This condition may require special care and planning for delivery.
Causes of Placenta Previa
Several factors can increase the risk of placenta previa. While the exact cause is not always clear, some common risk factors include:
Although these factors raise the risk, placenta previa can happen to anyone. Therefore, regular prenatal care is important for all pregnant women.
Symptoms of Placenta Previa
Placenta previa symptoms can vary. However, the most common sign is painless vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. Watch for these symptoms:
Sometimes, there are no symptoms until later in pregnancy. If you notice any bleeding, contact your doctor right away.
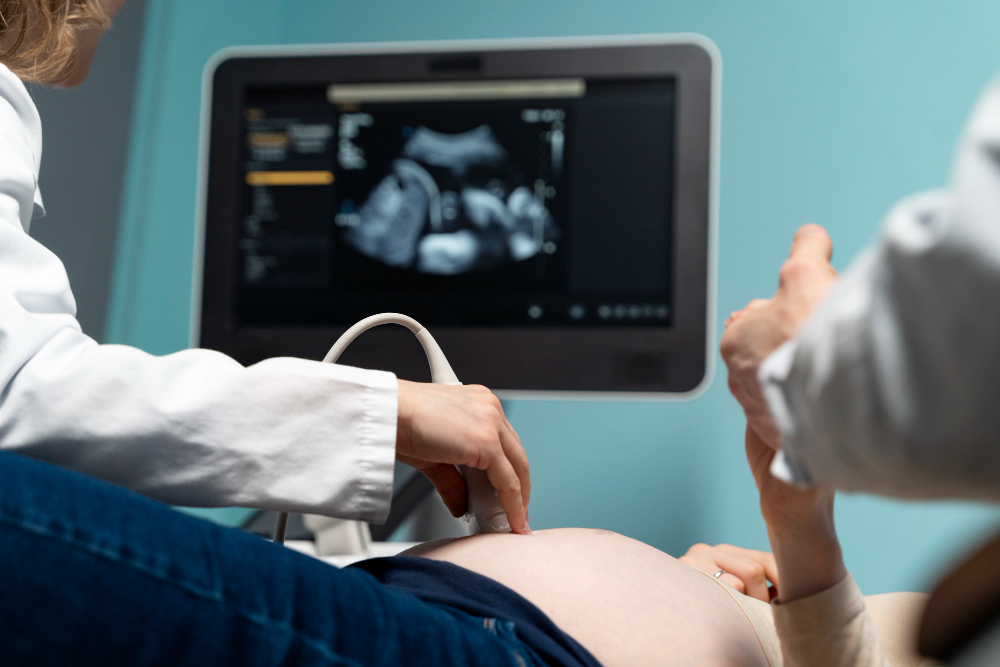
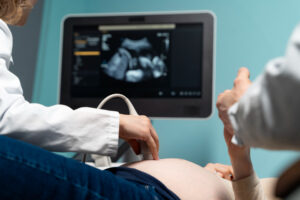
How Is Placenta Previa Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose placenta previa. Most often, it is found during a routine ultrasound. Here is how diagnosis usually happens:
Because placenta previa can change as pregnancy goes on, doctors may repeat ultrasounds to check the placenta’s position.
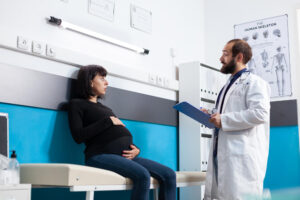
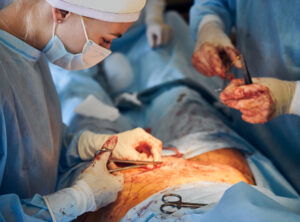
Treatment Options for Placenta Previa
Treatment for placenta previa depends on how far along the pregnancy is and how much bleeding occurs. Common placenta previa treatment options include:
Doctors will create a care plan based on your needs. Regular check-ups help keep both mother and baby safe.
Prevention and Lifestyle Guidance
While placenta previa cannot always be prevented, you can lower your risk by following healthy habits. Consider these tips:
Early care and healthy choices can make a big difference for you and your baby.
When to Seek Medical Help
It is important to know when to call your doctor. Seek medical help right away if you notice:
Prompt care can prevent serious problems and protect your health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Placenta Previa
If you have concerns about placenta previa, consult a healthcare specialist at Dr. Meenal Singh for personalized advice.